Classification
Routines for classification.
DawidSkene
Bases: BaseClassificationAggregator
The Dawid-Skene aggregation model is a probabilistic model that parametrizes the expertise level of workers with confusion matrices.
Let \(e^w\) be a worker confusion (error) matrix of size \(K \times K\) in case of the \(K\) class classification, \(p\) be a vector of prior class probabilities, \(z_j\) be a true task label, and \(y^w_j\) be a worker response to the task \(j\). The relationship between these parameters is represented by the following latent label model.
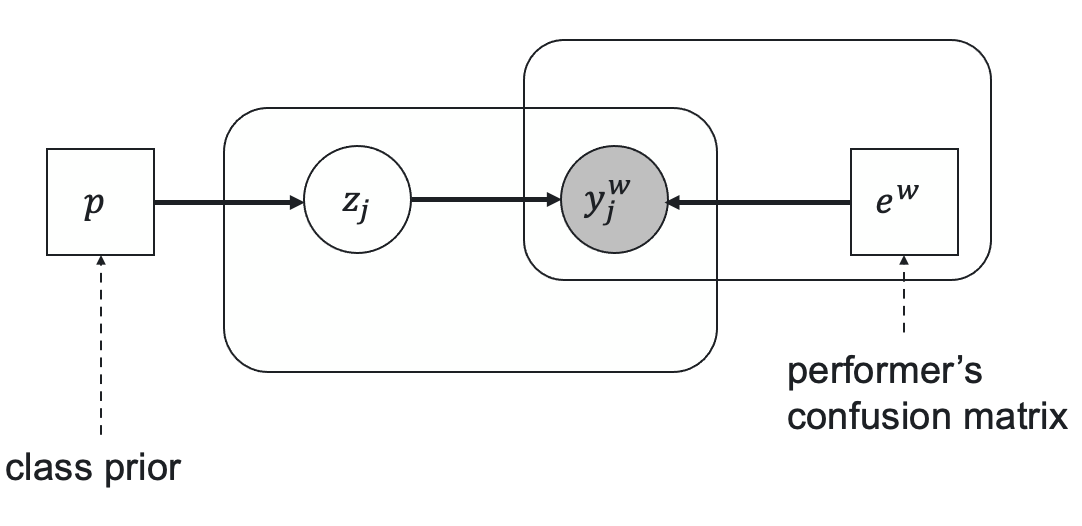
Here the prior true label probability is $$ \operatorname{Pr}(z_j = c) = p[c], $$ and the probability distribution of the worker responses with the true label \(c\) is represented by the corresponding column of the error matrix: $$ \operatorname{Pr}(y_j^w = k | z_j = c) = e^w[k, c]. $$
Parameters \(p\), \(e^w\), and latent variables \(z\) are optimized with the Expectation-Maximization algorithm: 1. E-step. Estimates the true task label probabilities using the specified workers' responses, the prior label probabilities, and the workers' error probability matrix. 2. M-step. Estimates the workers' error probability matrix using the specified workers' responses and the true task label probabilities.
A. Philip Dawid and Allan M. Skene. Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Observer Error-Rates Using the EM Algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series C (Applied Statistics), Vol. 28, 1 (1979), 20–28.
https://doi.org/10.2307/2346806
Examples:
>>> from crowdkit.aggregation import DawidSkene
>>> from crowdkit.datasets import load_dataset
>>> df, gt = load_dataset('relevance-2')
>>> ds = DawidSkene(100)
>>> result = ds.fit_predict(df)
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/dawid_skene.py
16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 | |
errors_: Optional[pd.DataFrame] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The workers' error matrices. The pandas.DataFrame data is indexed by worker and label with a column
for every label_id found in data so that result.loc[worker, observed_label, true_label] is the probability
that worker produces observed_label, given that the task true label is true_label.
loss_history_: List[float] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
A list of loss values during training.
n_iter: int = attr.ib(default=100)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The maximum number of EM iterations.
priors_: Optional[pd.Series[Any]] = named_series_attrib(name='prior')
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The prior label distribution.
The pandas.DataFrame data is indexed by task so that result.loc[task, label] is the probability that
the task true label is equal to label. Each probability is in the range from 0 to 1, all task probabilities
must sum up to 1.
probas_: Optional[pd.DataFrame] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The probability distributions of task labels.
The pandas.Series data is indexed by task so that labels.loc[task] is the most likely true label of tasks.
tol: float = attr.ib(default=1e-05)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The tolerance stopping criterion for iterative methods with a variable number of steps.
The algorithm converges when the loss change is less than the tol parameter.
fit(data)
Fits the model to the training data with the EM algorithm.
Args:
data (DataFrame): The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the pandas.DataFrame data containing task, worker, and label columns.
Returns:
DawidSkene: self.
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/dawid_skene.py
155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 | |
fit_predict(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns the aggregated results.
Args:
data (DataFrame): The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the pandas.DataFrame data containing task, worker, and label columns.
Returns:
Series: Task labels. The pandas.Series data is indexed by task so that labels.loc[task] is the most likely true label of tasks.
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/dawid_skene.py
221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 | |
fit_predict_proba(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns probability distributions of labels for each task.
Args:
data (DataFrame): The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the pandas.DataFrame data containing task, worker, and label columns.
Returns:
DataFrame: Probability distributions of task labels.
The pandas.DataFrame data is indexed by task so that result.loc[task, label] is the probability that the task true label is equal to label.
Each probability is in the range from 0 to 1, all task probabilities must sum up to 1.
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/dawid_skene.py
206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 | |
GLAD
Bases: BaseClassificationAggregator
The GLAD (Generative model of Labels, Abilities, and Difficulties) model is a probabilistic model that parametrizes the abilities of workers and the difficulty of tasks.
Let's consider a case of \(K\) class classification. Let \(p\) be a vector of prior class probabilities, \(\alpha_i \in (-\infty, +\infty)\) be a worker ability parameter, \(\beta_j \in (0, +\infty)\) be an inverse task difficulty, \(z_j\) be a latent variable representing the true task label, and \(y^i_j\) be a worker response that we observe. The relationships between these variables and parameters according to GLAD are represented by the following latent label model:
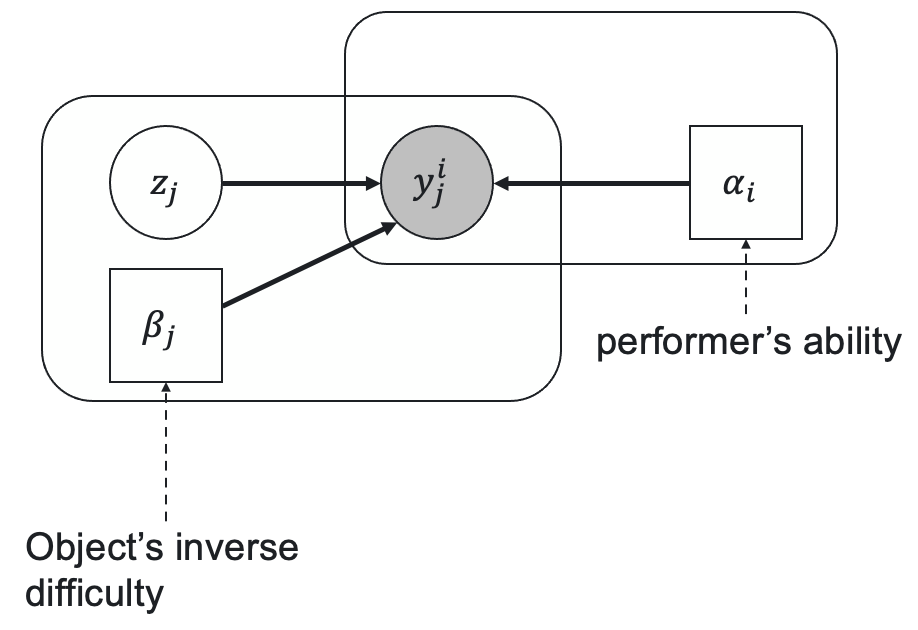
The prior probability of \(z_j\) being equal to \(c\) is $$ \operatorname{Pr}(z_j = c) = p[c], $$ and the probability distribution of the worker responses with the true label \(c\) follows the single coin Dawid-Skene model where the true label probability is a sigmoid function of the product of the worker ability and the inverse task difficulty: $$ \operatorname{Pr}(y^i_j = k | z_j = c) = \begin{cases}a(i, j), & k = c \ \frac{1 - a(i,j)}{K-1}, & k \neq c\end{cases}, $$ where $$ a(i,j) = \frac{1}{1 + \exp(-\alpha_i\beta_j)}. $$
Parameters \(p\), \(\alpha\), \(\beta\), and latent variables \(z\) are optimized with the Expectation-Minimization algorithm: 1. E-step. Estimates the true task label probabilities using the alpha parameters of workers' abilities, the prior label probabilities, and the beta parameters of task difficulty. 2. M-step. Optimizes the alpha and beta parameters using the conjugate gradient method.
J. Whitehill, P. Ruvolo, T. Wu, J. Bergsma, and J. Movellan. Whose Vote Should Count More: Optimal Integration of Labels from Labelers of Unknown Expertise. Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2009
https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2009/file/f899139df5e1059396431415e770c6dd-Paper.pdf
Examples:
>>> from crowdkit.aggregation import GLAD
>>> from crowdkit.datasets import load_dataset
>>> df, gt = load_dataset('relevance-2')
>>> glad = GLAD()
>>> result = glad.fit_predict(df)
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/glad.py
24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 | |
alphas_: pd.Series[Any] = named_series_attrib(name='alpha')
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The alpha parameters of workers' abilities.
The pandas.Series data is indexed by worker that contains the estimated alpha parameters.
alphas_priors_mean: Optional[pd.Series[Any]] = attr.ib(default=None)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The prior mean value of the alpha parameters.
betas_: pd.Series[Any] = named_series_attrib(name='beta')
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The beta parameters of task difficulty.
The pandas.Series data is indexed by task that contains the estimated beta parameters.
betas_priors_mean: Optional[pd.Series[Any]] = attr.ib(default=None)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The prior mean value of the beta parameters.
labels_priors: Optional[pd.Series[Any]] = attr.ib(default=None)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The prior label probabilities.
loss_history_: List[float] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
A list of loss values during training.
m_step_max_iter: int = attr.ib(default=25)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The maximum number of iterations of the conjugate gradient method in the M-step.
m_step_tol: float = attr.ib(default=0.01)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The tolerance stopping criterion of the conjugate gradient method in the M-step.
n_iter: int = attr.ib(default=100)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The maximum number of EM iterations.
probas_: Optional[pd.DataFrame] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The probability distributions of task labels.
The data frame is indexed by task so that result.loc[task, label] is the probability that the task
true label is equal to label. Each probability is in the range from 0 to 1, all task probabilities
must sum up to 1.
silent: bool = attr.ib(default=True)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
Specifies if the progress bar will be shown (false) or not (true).
tol: float = attr.ib(default=1e-05)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The tolerance stopping criterion for iterative methods with a variable number of steps.
The algorithm converges when the loss change is less than the tol parameter.
fit(data)
Fits the model to the training data with the EM algorithm.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
GLAD |
GLAD
|
self. |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/glad.py
312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 | |
fit_predict(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns the aggregated results.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Series |
Series[Any]
|
Task labels. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/glad.py
384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 | |
fit_predict_proba(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns probability distributions of labels for each task.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
DataFrame |
DataFrame
|
Probability distributions of task labels.
The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/glad.py
367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 | |
GoldMajorityVote
Bases: BaseClassificationAggregator
The Gold Majority Vote model is used when a golden dataset (ground truth) exists for some tasks. It calculates the probability of a correct label for each worker based on the golden set. After that, the sum of the probabilities of each label is calculated for each task. The correct label is the one with the greatest sum of the probabilities.
For example, you have 10 000 tasks completed by 3 000 different workers. And you have 100 tasks where you already
know the ground truth labels. First, you can call fit to calculate the percentage of correct labels for each worker.
And then call predict to calculate labels for your 10 000 tasks.
The following rules must be observed:
1. All workers must complete at least one task from the golden dataset.
2. All workers from the dataset that is submitted to predict must be included in the response dataset that is submitted to fit.
Examples:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from crowdkit.aggregation import GoldMajorityVote
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(
>>> [
>>> ['t1', 'p1', 0],
>>> ['t1', 'p2', 0],
>>> ['t1', 'p3', 1],
>>> ['t2', 'p1', 1],
>>> ['t2', 'p2', 0],
>>> ['t2', 'p3', 1],
>>> ],
>>> columns=['task', 'worker', 'label']
>>> )
>>> true_labels = pd.Series({'t1': 0})
>>> gold_mv = GoldMajorityVote()
>>> result = gold_mv.fit_predict(df, true_labels)
Attributes:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
labels_ |
Optional[Series]
|
The task labels. The |
skills_ |
Optional[Series]
|
The workers' skills. The |
probas_ |
Optional[DataFrame]
|
The probability distributions of task labels.
The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/gold_majority_vote.py
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 | |
fit(data, true_labels)
Fits the model to the training data.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
true_labels |
Series
|
The ground truth labels of tasks. The |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
GoldMajorityVote |
GoldMajorityVote
|
self. |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/gold_majority_vote.py
74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 | |
fit_predict(data, true_labels)
Fits the model to the training data and returns the aggregated results.
Args:
data (DataFrame): The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the pandas.DataFrame data containing task, worker, and label columns.
true_labels (Series): The ground truth labels of tasks. The `pandas.Series` data is indexed by `task`
so that `labels.loc[task]` is the task ground truth label.
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Series |
Series[Any]
|
The task labels. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/gold_majority_vote.py
125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 | |
fit_predict_proba(data, true_labels)
Fits the model to the training data and returns probability distributions of labels for each task.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
true_labels |
Series
|
The ground truth labels of tasks. The |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
DataFrame |
DataFrame
|
Probability distributions of task labels.
The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/gold_majority_vote.py
141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 | |
predict(data)
Predicts the true labels of tasks when the model is fitted.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Series |
Series[Any]
|
The task labels. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/gold_majority_vote.py
92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 | |
predict_proba(data)
Returns probability distributions of labels for each task when the model is fitted.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
DataFrame |
DataFrame
|
Probability distributions of task labels.
The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/gold_majority_vote.py
108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 | |
KOS
Bases: BaseClassificationAggregator
The KOS (Karger, Oh, and Shah 2011) aggregation model is an iterative algorithm that calculates the log-likelihood of the task being positive while modeling the worker reliability.
Let \(A_{ij}\) be a matrix of the responses of a worker \(j\) on a task \(i\). If the worker \(j\) does not respond to the task \(i\), then \(A_{ij} = 0\). Otherwise, \(|A_{ij}| = 1\). The algorithm operates on real-valued task messages \(x_{i \rightarrow j}\) and worker messages \(y_{j \rightarrow i}\). A task message \(x_{i \rightarrow j}\) represents the log-likelihood of task \(i\) being a positive task, and a worker message \(y_{j \rightarrow i}\) represents how reliable worker \(j\) is.
At \(k\)-th iteration, the values are updated as follows: $$ x_{i \rightarrow j}^{(k)} = \sum_{j^{'} \in \partial i \backslash j} A_{ij^{'}} y_{j^{'} \rightarrow i}^{(k-1)} \ y_{j \rightarrow i}^{(k)} = \sum_{i^{'} \in \partial j \backslash i} A_{i^{'}j} x_{i^{'} \rightarrow j}^{(k-1)} $$
David R. Karger, Sewoong Oh, and Devavrat Shah. Budget-Optimal Task Allocation for Reliable Crowdsourcing Systems. Operations Research 62.1 (2014), 1-38.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1110.3564
Examples:
>>> from crowdkit.aggregation import KOS
>>> from crowdkit.datasets import load_dataset
>>> df, gt = load_dataset('relevance-2')
>>> ds = KOS(10)
>>> result = ds.fit_predict(df)
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/kos.py
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 | |
n_iter: int = attr.ib(default=100)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The maximum number of iterations.
random_state: int = attr.ib(default=0)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The state of the random number generator.
fit(data)
Fits the model to the training data.
Args:
data (DataFrame): The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the pandas.DataFrame data containing task, worker, and label columns.
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
KOS |
KOS
|
self. |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/kos.py
51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 | |
fit_predict(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns the aggregated results.
Args:
data (DataFrame): The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the pandas.DataFrame data containing task, worker, and label columns.
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Series |
Series[Any]
|
The task labels. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/kos.py
113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 | |
MACE
Bases: BaseClassificationAggregator
The Multi-Annotator Competence Estimation (MACE) model is a probabilistic model that associates each worker with a label probability distribution. A worker can be spamming on each task. If the worker is not spamming, they label a task correctly. If the worker is spamming, they answer according to their probability distribution.
We assume that the correct label \(T_i\) comes from a discrete uniform distribution. When a worker annotates a task, they are spamming with probability \(\operatorname{Bernoulli}(1 - \theta_j)\). \(S_{ij}\) specifies whether or not worker \(j\) is spamming on instance \(i\). Thus, if the worker is not spamming on the task, i.e. \(S_{ij} = 0\), their response is the true label, i.e. \(A_{ij} = T_i\). Otherwise, their response \(A_{ij}\) is drawn from a multinomial distribution with parameter vector \(\xi_j\).

The model can be enhanced by adding the Beta prior on \(\theta_j\) and the Diriclet prior on \(\xi_j\).
The marginal data likelihood is maximized with the Expectation-Maximization algorithm:
1. E-step. Performs n_restarts random restarts, and keeps the model with the best marginal data likelihood.
2. M-step. Smooths parameters by adding a fixed value smoothing to the fractional counts before normalizing.
3. Variational M-step. Employs Variational-Bayes (VB) training with symmetric Beta priors on \(\theta_j\) and symmetric Dirichlet priors on the strategy parameters $\xi_j.
D. Hovy, T. Berg-Kirkpatrick, A. Vaswani and E. Hovy. Learning Whom to Trust with MACE. In Proceedings of NAACL-HLT, Atlanta, GA, USA (2013), 1120–1130.
https://aclanthology.org/N13-1132.pdf
Examples:
>>> from crowdkit.aggregation import MACE
>>> from crowdkit.datasets import load_dataset
>>> df, gt = load_dataset('relevance-2')
>>> mace = MACE()
>>> result = mace.fit_predict(df)
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/mace.py
70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 | |
alpha: float = attr.ib(default=0.5)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The prior parameter for the Beta distribution on $ heta_j$.
beta: float = attr.ib(default=0.5)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The prior parameter for the Beta distribution on $ heta_j$.
default_noise: float = attr.ib(default=0.5)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The default noise parameter for the initialization.
method: str = attr.ib(default='vb')
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The method which is used for the M-step. Either 'vb' or 'em'. 'vb' means optimization with Variational Bayes using priors. 'em' means standard Expectation-Maximization algorithm.
n_iter: int = attr.ib(default=50)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The maximum number of EM iterations for each optimization run.
n_restarts: int = attr.ib(default=10)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The number of optimization runs of the algorithms. The final parameters are those that gave the best log likelihood. If one run takes too long, this parameter can be set to 1.
probas_: Optional[pd.DataFrame] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The probability distributions of task labels.
The pandas.DataFrame data is indexed by task so that result.loc[task, label] is the probability that
the task true label is equal to label. Each probability is in the range from 0 to 1,
all task probabilities must sum up to 1.
random_state: int = attr.ib(default=0)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The state of the random number generator.
smoothing: float = attr.ib(default=0.1)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The smoothing parameter for the normalization.
smoothing_: float = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The smoothing parameter.
spamming_: NDArray[np.float64] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The posterior distribution of workers' spamming states.
strategy_priors_: Optional[NDArray[np.float64]] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The prior parameters for the Diriclet distribution on \(\xi_j\).
theta_priors_: Optional[NDArray[np.float64]] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The prior parameters for the Beta distribution on \(\theta_j\).
thetas_: NDArray[np.float64] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The posterior distribution of workers' spamming labels.
verbose: int = attr.ib(default=0)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
Specifies if the progress will be printed or not: 0 — no progress bar, 1 — only for restarts, 2 — for both restarts and optimization.
fit(data)
Fits the model to the training data.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
MACE |
MACE
|
The fitted MACE model. |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/mace.py
158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 | |
fit_predict(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns the aggregated results.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Series |
Series[Any]
|
Task labels. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/mace.py
257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 | |
fit_predict_proba(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns probability distributions of labels for each task.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
DataFrame |
DataFrame
|
Probability distributions of task labels.
The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/mace.py
273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 | |
MMSR
Bases: BaseClassificationAggregator
The Matrix Mean-Subsequence-Reduced Algorithm (M-MSR) model assumes that workers have different expertise levels and are represented as a vector of "skills" \(s\) which entries \(s_i\) show the probability that the worker \(i\) will answer the given task correctly. Having that, we can estimate the probability of each worker via solving a rank-one matrix completion problem as follows: $$ \mathbb{E}\left[\frac{M}{M-1}\widetilde{C}-\frac{1}{M-1}\boldsymbol{1}\boldsymbol{1}^T\right] = \boldsymbol{s}\boldsymbol{s}^T, $$ where \(M\) is the total number of classes, \(\widetilde{C}\) is a covariance matrix between workers, and \(\boldsymbol{1}\boldsymbol{1}^T\) is the all-ones matrix which has the same size as \(\widetilde{C}\).
Thus, the problem of estimating the skill level vector \(s\) becomes equivalent to the rank-one matrix completion problem. The M-MSR algorithm is an iterative algorithm for the robust rank-one matrix completion, so its result is an estimator of the vector \(s\). And the aggregation is weighted majority voting with weights equal to \(\log \frac{(M-1)s_i}{1-s_i}\).
Q. Ma and Alex Olshevsky. Adversarial Crowdsourcing Through Robust Rank-One Matrix Completion. 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2020)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12181
Examples:
>>> from crowdkit.aggregation import MMSR
>>> from crowdkit.datasets import load_dataset
>>> df, gt = load_dataset('relevance-2')
>>> mmsr = MMSR()
>>> result = mmsr.fit_predict(df)
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/m_msr.py
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 | |
loss_history_: List[float] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
A list of loss values during training.
n_iter: int = attr.ib(default=10000)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The maximum number of iterations.
random_state: Optional[int] = attr.ib(default=0)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The seed number for the random initialization.
scores_: Optional[pd.DataFrame] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The task label scores.
The pandas.DataFrame data is indexed by task so that result.loc[task, label] is a score of label for task.
skills_: Optional[pd.Series[Any]] = named_series_attrib(name='skill')
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The task labels.
The pandas.Series data is indexed by task so that labels.loc[task] is the most likely true label of tasks.
tol: float = attr.ib(default=1e-10)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The tolerance stopping criterion for iterative methods with a variable number of steps. The algorithm converges when the loss change is less than the tol parameter.
fit(data)
Fits the model to the training data.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
MMSR |
MMSR
|
self. |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/m_msr.py
103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 | |
fit_predict(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns the aggregated results.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Series |
Series[Any]
|
The task labels. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/m_msr.py
151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 | |
fit_predict_score(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns the total sum of weights for each label.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
DataFrame |
DataFrame
|
The task label scores. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/m_msr.py
165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 | |
predict(data)
Predicts the true labels of tasks when the model is fitted.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Series |
Series[Any]
|
The task labels. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/m_msr.py
119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 | |
predict_score(data)
Returns the total sum of weights for each label when the model is fitted.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
DataFrame |
DataFrame
|
The task label scores. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/m_msr.py
135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 | |
MajorityVote
Bases: BaseClassificationAggregator
The Majority Vote aggregation algorithm is a straightforward approach for categorical aggregation: for each task, it outputs a label with the largest number of responses. Additionaly, the Majority Vote can be used when different weights are assigned to workers' votes. In this case, the resulting label will have the largest sum of weights.
{% note info %}
If two or more labels have the largest number of votes, the resulting label will be the same for all tasks that have the same set of labels with the same number of votes.
{% endnote %}
Examples:
Basic Majority Vote:
>>> from crowdkit.aggregation import MajorityVote
>>> from crowdkit.datasets import load_dataset
>>> df, gt = load_dataset('relevance-2')
>>> result = MajorityVote().fit_predict(df)
Weighted Majority Vote:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from crowdkit.aggregation import MajorityVote
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(
>>> [
>>> ['t1', 'p1', 0],
>>> ['t1', 'p2', 0],
>>> ['t1', 'p3', 1],
>>> ['t2', 'p1', 1],
>>> ['t2', 'p2', 0],
>>> ['t2', 'p3', 1],
>>> ],
>>> columns=['task', 'worker', 'label']
>>> )
>>> skills = pd.Series({'p1': 0.5, 'p2': 0.7, 'p3': 0.4})
>>> result = MajorityVote().fit_predict(df, skills)
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/majority_vote.py
18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 | |
default_skill: Optional[float] = attr.ib(default=None)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
Default worker weight value.
on_missing_skill: str = attr.ib(default='error')
class-attribute
instance-attribute
A value which specifies how to handle assignments performed by workers with an unknown skill.
Possible values:
* error: raises an exception if there is at least one assignment performed by a worker with an unknown skill;
* ignore: drops assignments performed by workers with an unknown skill during prediction,
raises an exception if there are no assignments with a known skill for any task;
* value: the default value will be used if a skill is missing.
probas_: Optional[pd.DataFrame] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The probability distributions of task labels. The pandas.DataFrame data is indexed by task
so that result.loc[task, label] is the probability that the task true label is equal to label.
Each probability is in the range from 0 to 1, all task probabilities must sum up to 1.
skills_: Optional[pd.Series[Any]] = named_series_attrib(name='skill')
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The workers' skills. The pandas.Series data is indexed by worker and has the corresponding worker skill.
fit(data, skills=None)
Fits the model to the training data.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
skills |
Series
|
The workers' skills. The |
None
|
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
MajorityVote |
MajorityVote
|
self. |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/majority_vote.py
78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 | |
fit_predict(data, skills=None)
Fits the model to the training data and returns the aggregated results.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
skills |
Series
|
The workers' skills. The |
None
|
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Series |
Series[Any]
|
The task labels. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/majority_vote.py
131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 | |
fit_predict_proba(data, skills=None)
Fits the model to the training data and returns probability distributions of labels for each task.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
skills |
Series
|
The workers' skills. The |
None
|
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
DataFrame |
DataFrame
|
The probability distributions of task labels.
The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/majority_vote.py
110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 | |
OneCoinDawidSkene
Bases: DawidSkene
The one-coin Dawid-Skene aggregation model works exactly the same as the original Dawid-Skene model based on the EM algorithm, except for calculating the workers' errors at the M-step of the algorithm.
For the one-coin model, a worker confusion (error) matrix is parameterized by a single parameter \(s_w\): $$ e^w_{j,z_j} = \begin{cases} s_{w} & y^w_j = z_j \ \frac{1 - s_{w}}{K - 1} & y^w_j \neq z_j \end{cases} $$ where \(e^w\) is a worker confusion (error) matrix of size \(K \times K\) in case of the \(K\) class classification, \(z_j\) be a true task label, \(y^w_j\) is a worker response to the task \(j\), and \(s_w\) is a worker skill (accuracy).
In other words, the worker \(w\) uses a single coin flip to decide their assignment. No matter what the true label is, the worker has the \(s_w\) probability to assign the correct label, and has the \(1 − s_w\) probability to randomly assign an incorrect label. For the one-coin model, it suffices to estimate \(s_w\) for every worker \(w\) and estimate \(y^w_j\) for every task \(j\). Because of its simplicity, the one-coin model is easier to estimate and enjoys better convergence properties.
Parameters \(p\), \(e^w\), and latent variables \(z\) are optimized with the Expectation-Maximization algorithm: 1. E-step. Estimates the true task label probabilities using the specified workers' responses, the prior label probabilities, and the workers' error probability matrix. 2. M-step. Calculates a worker skill as their accuracy according to the label probability. Then estimates the workers' error probability matrix by assigning user skills to error matrix row by row.
Y. Zhang, X. Chen, D. Zhou, and M. I. Jordan. Spectral methods meet EM: A provably optimal algorithm for crowdsourcing. Journal of Machine Learning Research. Vol. 17, (2016), 1-44.
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1406.3824
Examples:
>>> from crowdkit.aggregation import OneCoinDawidSkene
>>> from crowdkit.datasets import load_dataset
>>> df, gt = load_dataset('relevance-2')
>>> hds = OneCoinDawidSkene(100)
>>> result = hds.fit_predict(df)
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/dawid_skene.py
235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 | |
fit(data)
Fits the model to the training data with the EM algorithm.
Args:
data (DataFrame): The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the pandas.DataFrame data containing task, worker, and label columns.
Returns:
DawidSkene: self.
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/dawid_skene.py
318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 | |
Wawa
Bases: BaseClassificationAggregator
The Worker Agreement with Aggregate (Wawa) algorithm consists of three steps: 1. calculates the majority vote label; 2. estimates workers' skills as a fraction of responses that are equal to the majority vote; 3. calculates the weigthed majority vote based on skills from the previous step.
Examples:
>>> from crowdkit.aggregation import Wawa
>>> from crowdkit.datasets import load_dataset
>>> df, gt = load_dataset('relevance-2')
>>> result = Wawa().fit_predict(df)
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/wawa.py
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 | |
probas_: Optional[pd.DataFrame] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The probability distributions of task labels.
The pandas.DataFrame data is indexed by task so that result.loc[task, label] is the probability that
the task true label is equal to label. Each probability is in the range from 0 to 1,
all task probabilities must sum up to 1.
skills_: Optional[pd.Series[Any]] = named_series_attrib(name='skill')
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The workers' skills.
The pandas.Series data is indexed by worker and has the corresponding worker skill.
fit(data)
Fits the model to the training data.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Wawa |
Wawa
|
self. |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/wawa.py
45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 | |
fit_predict(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns the aggregated results.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Series |
Series[Any]
|
The task labels. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/wawa.py
96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 | |
fit_predict_proba(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns probability distributions of labels for each task.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
DataFrame |
DataFrame
|
Probability distributions of task labels.
The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/wawa.py
110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 | |
predict(data)
Predicts the true labels of tasks when the model is fitted.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Series |
Series[Any]
|
The task labels. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/wawa.py
63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 | |
predict_proba(data)
Returns probability distributions of labels for each task when the model is fitted.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
DataFrame |
DataFrame
|
Probability distributions of task labels.
The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/wawa.py
79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 | |
ZeroBasedSkill
Bases: BaseClassificationAggregator
The Zero-Based Skill (ZBS) aggregation model performs weighted majority voting on tasks. After processing a pool of tasks, it re-estimates the workers' skills with a gradient descend step to optimize the mean squared error of the current skills and the fraction of responses that are equal to the aggregated labels.
This process is repeated until the labels change or exceed the number of iterations.
{% note info %}
It is necessary that all workers in the dataset that is sent to predict exist in responses to
the dataset that was sent to fit.
{% endnote %}
Examples:
>>> from crowdkit.aggregation import ZeroBasedSkill
>>> from crowdkit.datasets import load_dataset
>>> df, gt = load_dataset('relevance-2')
>>> result = ZeroBasedSkill().fit_predict(df)
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/zero_based_skill.py
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 | |
eps: float = 1e-05
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The convergence threshold.
lr_init: float = 1.0
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The initial learning rate.
lr_reduce_factor: float = 0.5
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The factor by which the learning rate will be multiplied every lr_steps_to_reduce step.
lr_steps_to_reduce: int = 20
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The number of steps required to reduce the learning rate.
n_iter: int = 100
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The maximum number of iterations.
probas_: Optional[pd.DataFrame] = attr.ib(init=False)
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The probability distributions of task labels.
The pandas.DataFrame data is indexed by task so that result.loc[task, label] is the probability that
the task true label is equal to label. Each probability is in the range from 0 to 1,
all task probabilities must sum up to 1.
skills_: Optional[pd.Series[Any]] = named_series_attrib(name='skill')
class-attribute
instance-attribute
The workers' skills.
The pandas.Series data is indexed by worker and has the corresponding worker skill.
fit(data)
Fits the model to the training data.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ZeroBasedSkill |
ZeroBasedSkill
|
self. |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/zero_based_skill.py
74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 | |
fit_predict(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns the aggregated results.
Args:
data (DataFrame): The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the pandas.DataFrame data containing task, worker, and label columns.
Returns:
Series: The task labels. The pandas.Series data is indexed by task
so that labels.loc[task] is the most likely true label of tasks.
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/zero_based_skill.py
139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 | |
fit_predict_proba(data)
Fits the model to the training data and returns the aggregated results.
Args:
data (DataFrame): The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the pandas.DataFrame data containing task, worker, and label columns.
Returns:
Series: The task labels. The pandas.Series data is indexed by task
so that labels.loc[task] is the most likely true label of tasks.
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/zero_based_skill.py
151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 | |
predict(data)
Predicts the true labels of tasks when the model is fitted.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Series |
Series[Any]
|
The task labels. The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/zero_based_skill.py
106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 | |
predict_proba(data)
Returns probability distributions of labels for each task when the model is fitted.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
data |
DataFrame
|
The training dataset of workers' labeling results
which is represented as the |
required |
Returns:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
DataFrame |
DataFrame
|
The probability distributions of task labels.
The |
Source code in crowdkit/aggregation/classification/zero_based_skill.py
122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 | |